India’s 43 UNESCO World Heritage Sites
The UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972, works globally to recognize and protect sites of significant cultural and natural importance. Recently, India has added two more sites to its UNESCO World Heritage list, bringing the total number of such sites in the country to 43. This achievement places India sixth among countries with the highest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites worldwide.
Out of these 43 sites, 35 are cultural, 7 are natural, and 1 is a mixed site that combines both cultural and natural significance.
In other words, UNESCO recognizes these 43 Indian sites as having exceptional universal value, deserving protection for future generations. These sites include ancient temples, forts, palaces, caves, national parks, and wildlife sanctuaries. They beautifully showcase India’s rich cultural and natural heritage and are must-visit destinations for every traveler.
As confirmed until December 2024, here is the updated overview:
- Total Sites: 43
- Cultural Sites: 35
- Natural Sites: 7
- Mixed Site: 1
📌 Recently Added Sites:
- Santiniketan (West Bengal) – 2023
- Hoysala Temples Group (Karnataka) – 2023
- Moidams – Ahom Royal Burial Grounds (Assam) – 2024
🏛️ Cultural Heritage Sites (Selected Highlights):
✓ Ajanta Caves (Maharashtra) – 1983
✓ Ellora Caves (Maharashtra) – 1983
✓ Agra Fort (Uttar Pradesh) – 1983
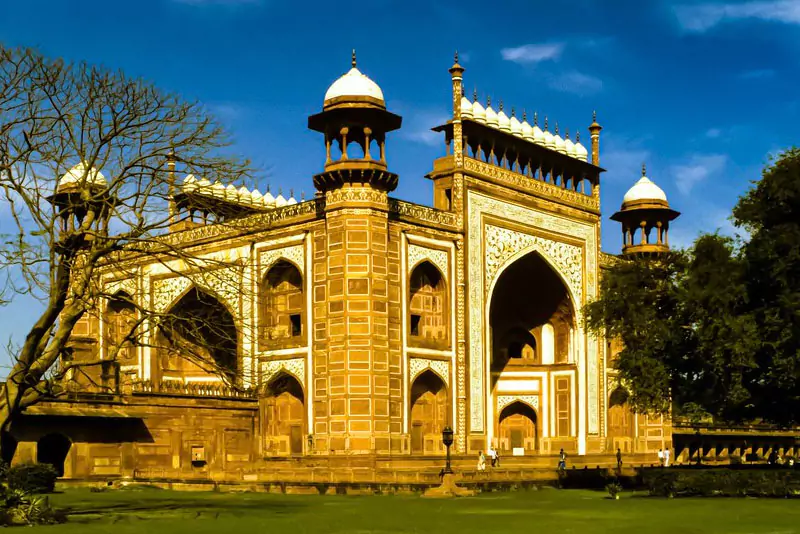
✓ Taj Mahal (Uttar Pradesh) – 1983
✓ Sun Temple, Konark (Odisha) – 1984
✓ Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram (Tamil Nadu) – 1984
✓ Churches and Convents of Goa – 1986
✓ Group of Monuments at Khajuraho (Madhya Pradesh) – 1986
✓ Group of Monuments at Hampi (Karnataka) – 1986
✓ Fatehpur Sikri (Uttar Pradesh) – 1986
✓ Elephanta Caves (Maharashtra) – 1987
✓ Great Living Chola Temples (Tamil Nadu) – 1987
✓ Group of Monuments at Pattadakal (Karnataka) – 1987
✓ Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi (Madhya Pradesh) – 1989
✓ Humayun’s Tomb (Delhi) – 1993
✓ Qutub Minar and its Monuments (Delhi) – 1993
✓ Mahabodhi Temple Complex, Bodh Gaya (Bihar) – 2002
✓ Bhimbetka Rock Shelters (Madhya Pradesh) – 2003
✓ Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (Maharashtra) – 2004
✓ Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park (Gujarat) – 2004
✓ Red Fort Complex (Delhi) – 2007
✓ Jantar Mantar (Delhi) – 2010
✓ Hill Forts of Rajasthan – 2013
✓ Rani ki Vav (Queen’s Stepwell) (Gujarat) – 2014
✓ Nalanda Mahavihara (Bihar) – 2016
✓ Le Corbusier’s Capitol Complex, Chandigarh – 2016
✓ Historic City of Ahmedabad (Gujarat) – 2017
✓ Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai – 2018
✓ Jaipur – The Pink City – 2019
✓ Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple (Telangana) – 2021
✓ Dholavira – Harappan City (Indus Valley Civilization) (Gujarat) – 2021
📍 Recently Added Cultural Sites:
- Santiniketan (West Bengal) – 2023
- Hoysala Temples Group: Belur, Halebidu, Somanathapura (Karnataka) – 2023
- Moidams – Ahom Royal Burial Grounds (Assam) – 2024
This comprehensive list reflects India’s immense historical, architectural, spiritual, and natural diversity — making these sites essential destinations for travelers seeking to explore India’s heritage on a global scale.
🌿 Natural Heritage Sites in India
- Kaziranga National Park (Assam) – 1985
Famous for its population of the Indian one-horned rhinoceros, Kaziranga offers a unique wildlife experience in its vast grasslands and wetlands. - Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) – 1985
Also known as Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary, this park is a paradise for bird watchers, especially during the migratory season. - Manas Wildlife Sanctuary (Assam) – 1985
A UNESCO-listed tiger and elephant reserve known for its biodiversity and stunning natural beauty. - Sundarbans National Park (West Bengal) – 1987
The world’s largest mangrove forest, home to the elusive Royal Bengal tiger and a rich variety of flora and fauna. - Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks (Uttarakhand) – 1988
Famous for its alpine flowers and rugged mountain terrain, this site offers breathtaking trekking and nature exploration opportunities. - Western Ghats (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu) – 2012
A mountain range known for its rich biodiversity and endemic species, ideal for nature lovers and adventure seekers. - Great Himalayan National Park (Himachal Pradesh) – 2014
A pristine wilderness offering trekking, wildlife viewing, and spectacular Himalayan landscapes.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites by State (2024)
| State / Union Territory | UNESCO World Heritage Sites | Total Sites |
| Uttar Pradesh | Taj Mahal, Fatehpur Sikri, Agra Fort | 3 |
| Maharashtra | Ajanta Caves, Ellora Caves, Elephanta Caves, Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus | 4 |
| Delhi | Qutub Minar Complex, Humayun’s Tomb, Red Fort, Jantar Mantar | 4 |
| Karnataka | Hampi, Pattadakal, Hoysala Temple Complex | 3 |
| Madhya Pradesh | Sanchi, Bhimbetka, Khajuraho | 3 |
| Gujarat | Champaner-Pavagadh, Rani ki Vav, Ahmedabad (Historic City), Dholavira | 4 |
| Rajasthan | Keoladeo National Park, Hill Forts of Rajasthan, Fatehpur Sikri* | 3 |
| Tamil Nadu | Mahabalipuram, Brihadeeswarar Temple, Nilgiri Mountains (part of Western Ghats)* | 2 + 1* |
| Bihar | Nalanda, Mahabodhi Temple | 2 |
| Assam | Manas, Kaziranga, Maidams (Ahom Royal Tombs) | 3 |
| West Bengal | Sundarbans, Shantiniketan | 4 |
| Kerala | Western Ghats (part), Nilgiri Hills (part of WHS) | 1 + 1* |
| Telangana | Ramappa Temple | 1 |
| Sikkim | Khangchendzonga National Park | 1 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Great Himalayan National Park | 1 |
| Uttarakhand | Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks | 1 |
| Goa | Churches and Convents of Goa | 1 |
| Chandigarh (UT) | Le Corbusier’s Capitol Complex | 1 |
| Mumbai (MH) | Victorian and Art Deco Ensemble | 1 |
| Jaipur (Rajasthan) | Jaipur – The Pink City | 1 |
📌 Notes:
Some sites span multiple states, such as the Western Ghats (covering 4 states) and the Hill Forts of Rajasthan (across several districts).
WHS = Part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site
Criteria for UNESCO World Heritage Site Selection:
- Testament to human creative genius
Exchange of cultural values - Expression of cultural traditions
- Evidence of human history
- Traditional human settlements
- Associated with significant global events
- Exceptional natural phenomena or beauty
- Important stages of Earth’s history
- Ecological and biological processes
- Important natural habitats for biodiversity
✅ Quick Facts:
- Maharashtra and Gujarat have the highest number of sites with 4 each.
- Delhi also has 4 prominent heritage sites.
- Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Rajasthan each have 3 sites.
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites are spread across 18 states and 2 union territories in India.
This breakdown helps travelers plan their visits across India’s culturally rich and diverse heritage locations, offering a glimpse into India’s vast historical, architectural, and natural treasures.